Abstract
Introduction.
The prognosis of patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is poor. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is approved for R/R DLBCL (≥3 rd line) in Spain since April 2019, based on data from single-arm phase 2 trials that showed complete response (CR) rates between 40-50% and prolonged remissions in 30-40% of patients. Real-world (RW) data from different countries have shown similar efficacy to pivotal trials, but there are no studies focused on the global Spanish experience, including different constructs with a large number of patients and no comparative studies have been carried out in Spain between commercial CAR-T therapy and the standard treatment of the pre-CAR era.
Methods
This is a multicenter, retrospective, observational study that included all patients with R/R DLBCL treated with CAR-T therapy who were registered in the GELTAMO/GETH database of patients treated with CAR-T therapy in Spain (n=255). The main objective was to analyze efficacy in terms of response rates and survival and analyze prognostic factors influencing survival. In addition, this cohort was compared with a historical population of R/R DLBCL patients from the GELTAMO-IPI study (Montalbán et al, Br J Haematol 2017), treated in the pre-CAR era (n = 158). From both cohorts, refractory patients according to the Scholar-1 criteria (primary refractoriness, refractoriness to last treatment, or early relapse after autologous stem-cell transplant) were identified and included in the comparative analysis.
Results
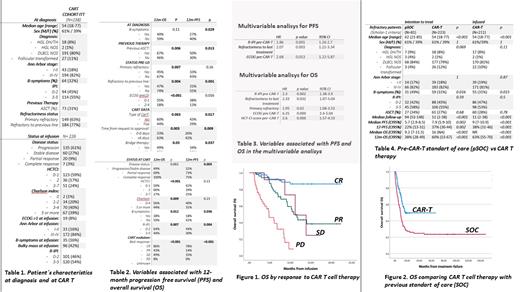
Characteristics of the CAR-T group at diagnosis and at infusion are shown in Table 1. From the 255 patients registered, 13 were excluded due to absence of follow up data and 4 for mantle cell lymphoma histology. Finally, 238 patients were included in the intention-to-treat analysis and 226 received the CAR-T infusion (124 axicabtagene ciloleucel, 101 tisagenlecleucel and 1 lisocabtagenemaraleucel). Median time from official approval to infusion was 60 days (34-363), and median time from apheresis to infusion was 46 days (16-349). Regarding adverse events of special interest, 79% of patients had cytokine release syndrome (7% ≥ grade 3), and 32% of patients had neurotoxicity (13.7% ≥ grade 3). Best response rates after CAR-T infusion were: CR 42%, partial response (PR) 27%, stable disease (SD) 7% and progressive disease (PD) 24%. With a median follow up from infusion of 8 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3.5 months (95% CI: 1.9-5), and median overall survival (OS) was not reached, with a 12-month OS of 53% (95% CI: 45-62); 12-month OS and PFS for patients who achieved CR was 86% (Figure 1) and 78% respectively. Factors influencing PFS and OS in the univariate analysis are shown in table 2. In the multivariate analysis, the factors with independent influence on both PFS and OS were R-IPI and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group-Performance status (ECOG-PS) pre-CAR, and presence of refractory disease to last treatment, as shown in table 3.
Regarding the comparative analysis with the historical cohort, the groups were well balanced, except for age and median follow up (Table 4). The survival for this analysis was calculated since the failure to last treatment. Patients treated with CAR T-cells vs standard of care pre-CAR had significantly better PFS (median of 7.9 vs 5.7 months, p=0.002), and OS (median of 16 vs 9.2, p<0.001).
Conclusions:
We conclude that efficacy results obtained from RW CAR T-cell therapy in Spain are comparable to the pivotal trials. The results of the comparative analysis suggest that the efficacy of CAR-T therapy in refractory patients is superior to that of the treatments available in the pre-CAR era.
Bastos-Oreiro: F. Hoffmann-La Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Kite: Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Honoraria; BMS-Celgene: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Reguera: Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Novartis: Speakers Bureau; BMS-Celgene, Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Iacoboni: BMS/Celgene, Gilead, Novartis, Janssen, Roche: Honoraria. Corral: Gilead: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Gileqd: Honoraria. Terol: Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel; Roche: Consultancy; Hospital Clinico Valencia: Current Employment; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel. Ortiz-Maldonado: Kite, Novartis, BMS, Janssen: Honoraria. Mussetti: Gilead: Other: Unspecified, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Unspecified; Takeda: Honoraria. Luzardo Henriquez: Kyte/Gilead. Takeda. Roche: Honoraria. Sancho: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol-Myers-Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Honoraria; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Salar: Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. Herrero: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Sureda: Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Bluebird: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Mundipharma: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Support for attending meetings and/or travel, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Barba: Novartis: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria. Kwon: Novartis, Celgene, Gilead, Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria. Martin Garcia-Sancho: Celgene: Honoraria, Other: travel; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel/Accommodations/Expenses; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel/Accommodations/Expenses; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Morphosys: Consultancy; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy; Clinigen: Consultancy; Eusa Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Takeda: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy; Kern Pharma: Other: TRAVEL, ACCOMMODATIONS, EXPENSES (paid by any for-profit health care company).

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal